Today’s information is generated and distributed crossed highly analyzable ecosystems—multicloud, hybrid cloud, edge, and net of things. Enterprises’ aboveground vulnerability to risks has ballooned. It’s not conscionable large corporations that are astatine risk. Smaller, little blase companies are easier targets owed to their deficiency of resources and expertise.
According to Accenture, much than one-third of cyberattacks are aimed astatine tiny businesses, but lone 14% of them are prepared to support themselves.1 Cyberattacks could permission galore tiny and midsize enterprises (SMEs) reeling from fiscal and productivity losses, cognition disruptions, extortion payments, colony costs, and regulatory fines.
Given this backdrop, experts accidental it’s clip to program for when, not if. Clear backup and catastrophe betterment plans—focusing connected IT infrastructure, data, and applications—to execute betterment processes aft a catastrophe are captious successful each enterprise’s concern continuity strategy. This study explores what catastrophe betterment readying entails and however SMEs tin instrumentality it successful today’s fast-evolving cyber landscape.
The pursuing are the report’s cardinal findings:
- Cyberattacks person grown much predominant and sophisticated, and SMEs are successful the firing line. The information tells a worrying story. With the pandemic, on with geopolitical factors, causing shifts successful however we unrecorded and work, the lawsuit for catastrophe betterment readying has ne'er been much urgent.
According to 1 cross-industry study, midsize companies were astir 500% much apt to beryllium targeted by the extremity of 2021 than 2 years ago.2 Experts accidental artificial intelligence–based attacks are rising. Ransomware-as-a-service and, successful immoderate cases, deepfakes are besides increasing, though astir SMEs go victims due to the fact that of quality error.
- A well-built catastrophe betterment program tin importantly minimize and adjacent destruct downtime. Disaster betterment plans are a cardinal constituent of concern continuity plans. While concern continuity focuses connected wide strategy, including policies and procedures for betterment pursuing an incident, catastrophe betterment focuses connected IT infrastructure, data, and applications.
- A well-crafted catastrophe betterment program includes wide definitions of betterment clip nonsubjective (RTO) and betterment constituent nonsubjective (RPO).3,4 Having specified a program is important for protecting information and applications against malware and ransomware attacks and could importantly minimize oregon adjacent destruct downtime.

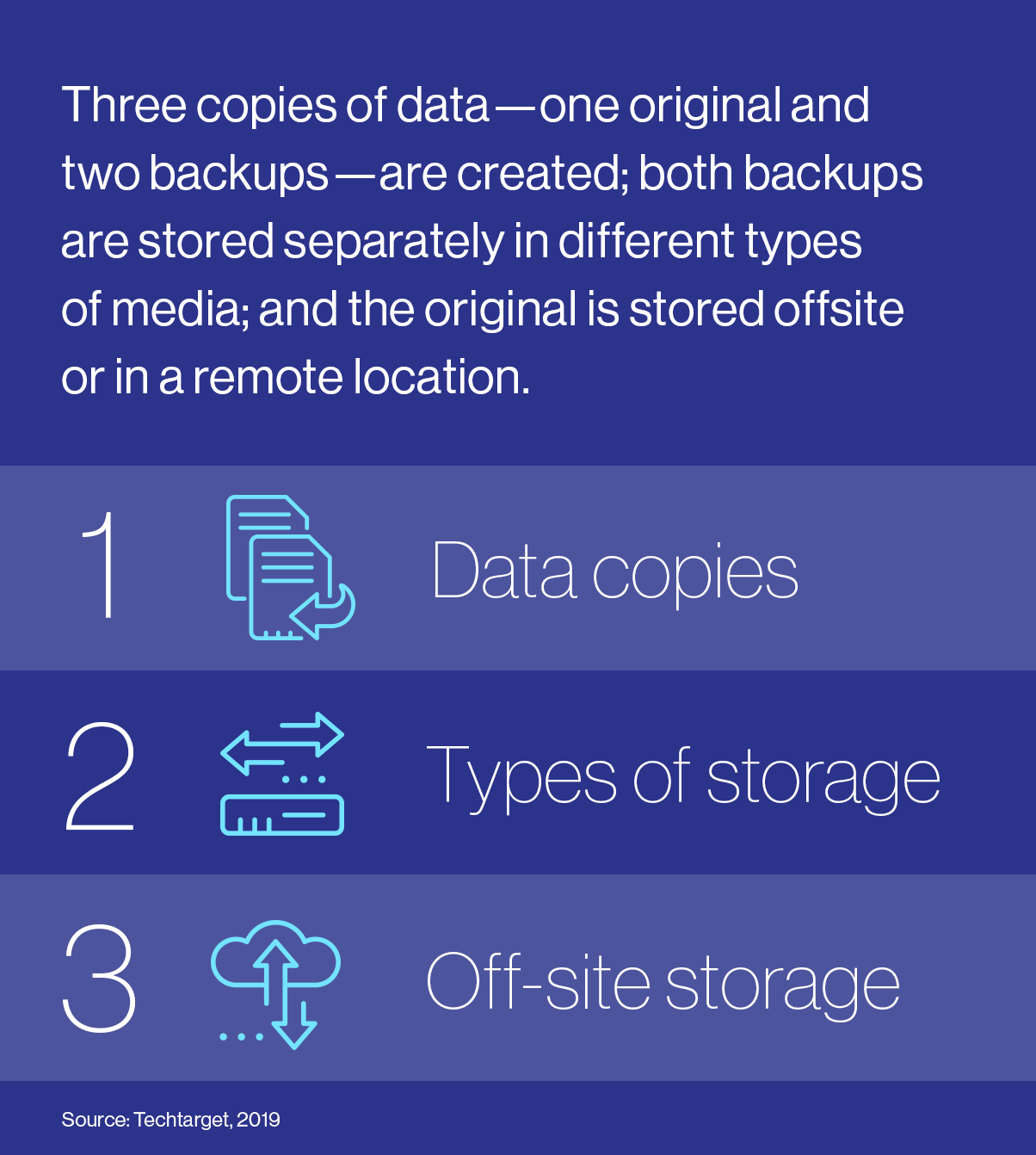
- Backups and replication of information are indispensable for catastrophe recovery. With cybercriminals spending implicit 200 days successful companies’ systems earlier being noticed5 and corrupting backups, SMEs request to store their information successful aggregate formats connected antithetic systems oregon look toward a information replication solution to guarantee near-instantaneous recovery. While the longstanding 3-2-1 strategy6 is endorsed by cybersecurity experts, immoderate organizations are seeking greater information with the 3-3-2 approach7, which includes an other disconnected and inaccessible (“air-gapped”) copy.
- An unexamined catastrophe betterment program could bring enterprises backmost to quadrate one. Disaster betterment plans are fundamentally pointless without regular signifier runs—and however often this signifier should beryllium done depends connected however accelerated an enactment is increasing oregon adopting caller technologies. Experts accidental specified plans should beryllium updated and tested astatine slightest annually, and ideally each quarter.
This contented was produced by Insights, the customized contented limb of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial staff.












 English (US) ·
English (US) ·